Section 1 Data engineering
1.1 purf package installization
purf is a Python package that adapts the ensemble and tree modules from scikit-learn (version 0.24.2). The package implements and modifies the positive-unlabeled random forest (PURF) algorithm proposed by Li and Hua (Li and Hua 2014; Denis, Gilleron, and Letouzey 2005; De Comité et al. 1999).
In bash:
- Create and activate Conda environment
conda create -n purf scikit-learn=0.24.2 numpy=1.19.0 cython=0.29.21 pandas=1.3.2
conda activate purf- Download package
cd purf- Install package
python setup.py install1.2 Retrieving P. falciparum protein variables
In bash:
echo "create database pf_reverse_vaccinology" | mariadb -u <dbuser> -p
mariadb -u <dbuser> -p pf_reverse_vaccinology < ./data/supplementary_data_1_pf_reverse_vaccinology.sqlOverall database schema:
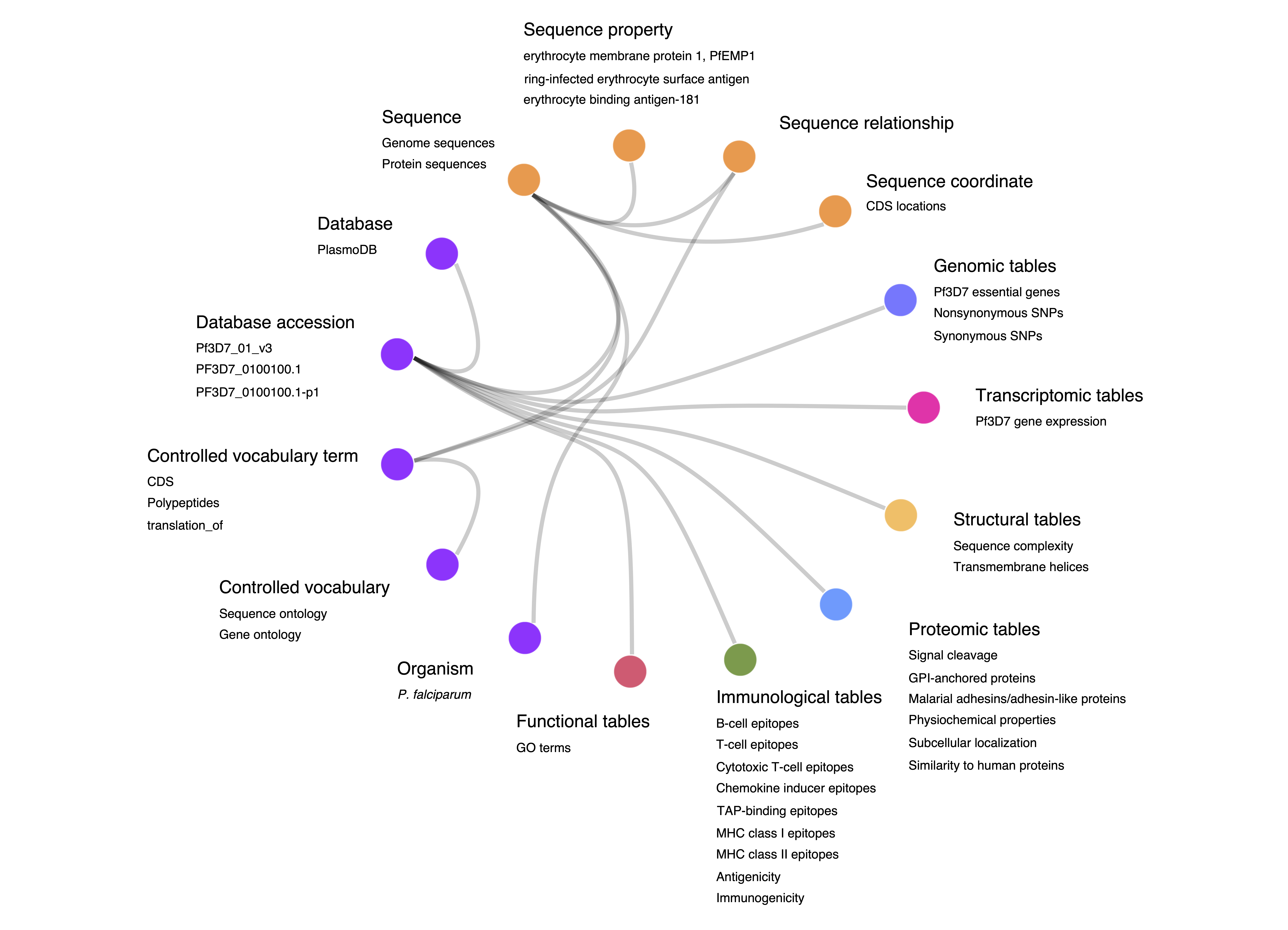
Detailed database structure:

In R:
library(RMariaDB)
library(DBI)
library(rlist)output_path <- "./other_data/pf_assembled_data.csv"
db <- dbConnect(RMariaDB::MariaDB(), user = "root", password = "", dbname = "pf_reverse_vaccinology")
get_data <- function(table_name, db) {
sql <- sqlInterpolate(db, "SELECT * FROM ?table", table = dbQuoteIdentifier(db, table_name))
return(subset(dbGetQuery(db, sql), select = -c(id)))
}
# protein ID and transcript ID map table
id_map <- dbGetQuery(db, 'SELECT dbxref_1.accession AS accession, dbxref_1.dbxref_id AS protein_id FROM dbxref AS dbxref_1
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature AS feature_1 ON dbxref_1.dbxref_id = feature_1.dbxref_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN cvterm ON feature_1.type_id = cvterm.cvterm_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature_relationship ON feature_1.feature_id = feature_relationship.subject_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature AS feature_2 ON feature_relationship.object_id = feature_2.feature_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN dbxref AS dbxref_2 ON feature_2.dbxref_id = dbxref_2.dbxref_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN organism ON feature_1.organism_id = organism.organism_id
WHERE feature_1.is_obsolete = 0 AND cvterm.name = "polypeptide" AND organism.species="falciparum_3D7"')1.2.1 Immunological data sets

In R:
immu <- list()
# predivac_processed result for T-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("predivac_processed", db))
# bepipred_2_0 result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("bepipred_2_0_processed", db))
# bepipred_1_0 result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("bepipred_1_0_processed", db))
# abcpred result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("abcpred_processed", db))
# ctlpred result for cytotoxic T-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("ctlpred_processed", db))
# il_10pred result for interleukine-10 inducing epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("il_10pred_processed", db))
# ifnepitope result for IFN-gamma inducing epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("ifnepitope_processed", db))
# tappred for high binding affinity epitopes toward the TAP transporter
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("tappred_processed", db))
# mhc_i for MHC class I epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("mhc_i", db))
# mhc_ii for MHC class II epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("mhc_ii", db))
# antigenicity
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("antigenicity", db))
# immunogenicity
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("immunogenicity", db))
# merge immunological data sets
immunological_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in immu) {
immunological_ds <- merge(x = immunological_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.2 Proteomic data sets
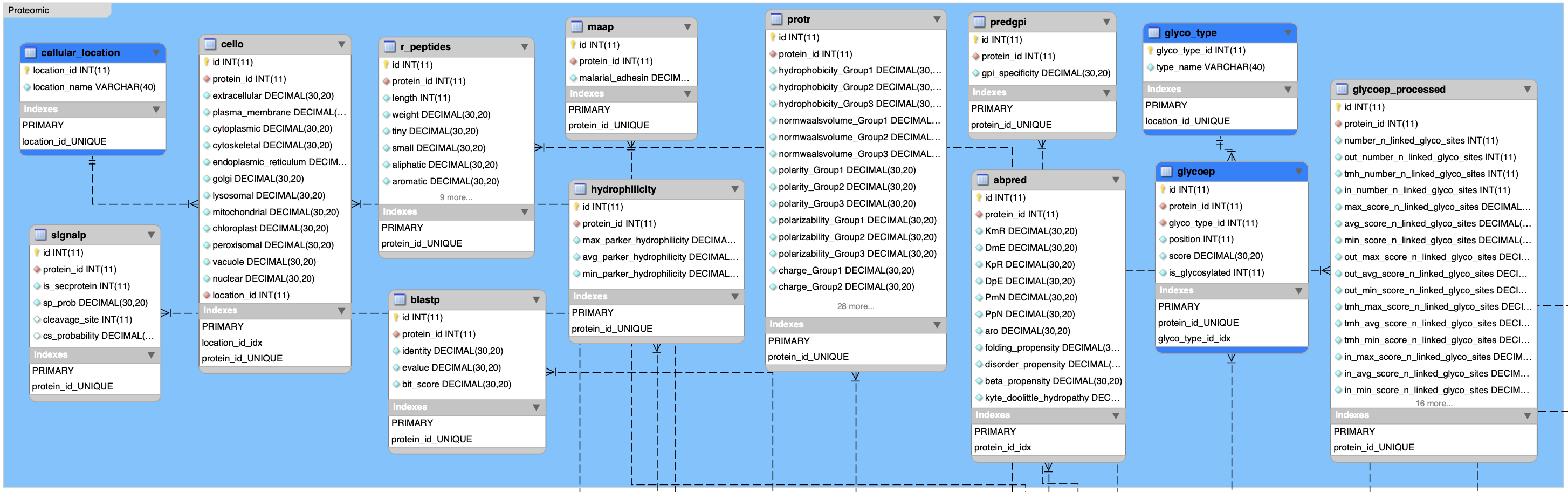
In R:
pro <- list()
# cello result for subcellualr localization
pro <- list.append(pro, subset(get_data("cello", db), select = -c(location_id)))
# maap result for malaria adhesin/adhesin-like proteins
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("maap", db))
# peptides result for physicochemical properties
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("r_peptides", db))
# protr result for physicochemical properties
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("protr", db))
# hydrophilicity
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("hydrophilicity", db))
# predgpi result for gpi anchors prediction
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("predgpi", db))
# signalp result for signal cleavage prediction
pro <- list.append(pro, subset(get_data("signalp", db), select = -c(is_secprotein, cleavage_site, cs_probability)))
# abpred results for amino acid compositions and other variables
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("abpred", db))
# glycoep results for N-linked and O-linked glycosylation
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("glycoep_processed", db))
# blastp result for similarity to human proteins
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("blastp", db))
# merge proteomic data sets
proteomic_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in pro) {
proteomic_ds <- merge(x = proteomic_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.3 Structural data sets
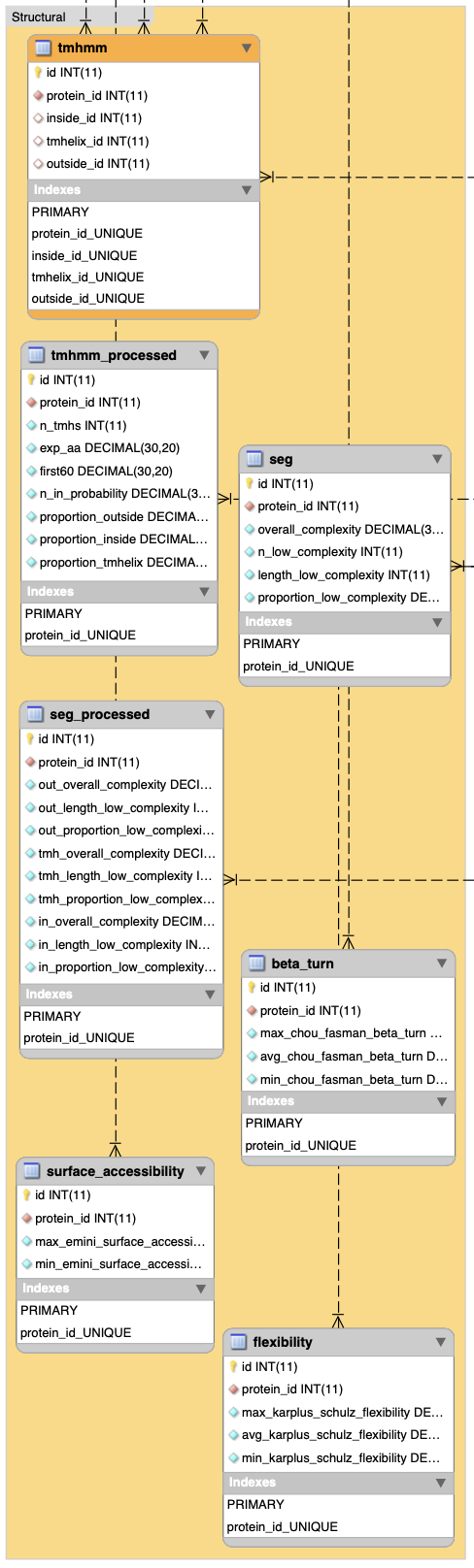
In R:
struc <- list()
# tmhmm result for transmembrane helices prediction
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("tmhmm_processed", db))
# seg result for sequence complexity
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("seg", db))
# seg + tmhmm result
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("seg_processed", db))
# b_cell_epitope_methods for structural predictions
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("beta_turn", db))
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("surface_accessibility", db))
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("flexibility", db))
# merge structural analysis data sets
structural_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in struc) {
structural_ds <- merge(x = structural_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.4 Genomic data sets

In R:
geno <- list()
# snp result
geno <- list.append(geno, get_data("snp", db))
# merge structural analysis data sets
genomic_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in geno) {
genomic_ds <- merge(x = genomic_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.5 Final assembly
In R:
# prepare predictor variables
data <- merge(x = immunological_ds, y = proteomic_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = data, y = structural_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = data, y = genomic_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = id_map, y = data, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
accession <- data$accession
data <- subset(data, select = -c(protein_id, accession))
rownames(data) <- accession
# write to output
write.csv(data, output_path)
# close database connection
dbDisconnect(db)1.3 Generating ML input
In R:
response_var <- read.csv("./other_data/pf_antigen_labels.csv", row.names = 1)
predictor_vars <- read.csv("./other_data/pf_assembled_data.csv", row.names = 1)
ml_input <- merge(x = response_var, y = predictor_vars, by = "row.names", all = TRUE)
row_names <- ml_input$Row.names
ml_input <- subset(ml_input, select = -c(Row.names))
rownames(ml_input) <- row_names
# write to output
write.csv(ml_input, "./data/supplementary_data_3_pf_ml_input.csv")sessionInfo()## R version 4.2.3 (2023-03-15)
## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit)
## Running under: macOS Big Sur ... 10.16
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
## LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
##
## locale:
## [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] rlist_0.4.6.2 DBI_1.1.3 RMariaDB_1.2.2
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] Rcpp_1.0.9 bslib_0.4.0 compiler_4.2.3 jquerylib_0.1.4
## [5] highr_0.9 R.methodsS3_1.8.2 R.utils_2.12.0 tools_4.2.3
## [9] digest_0.6.29 bit_4.0.4 jsonlite_1.8.0 evaluate_0.16
## [13] lifecycle_1.0.3 R.cache_0.16.0 pkgconfig_2.0.3 rlang_1.1.0
## [17] cli_3.6.1 rstudioapi_0.14 yaml_2.3.5 xfun_0.32
## [21] fastmap_1.1.0 styler_1.8.0 stringr_1.4.1 knitr_1.40
## [25] sass_0.4.2 vctrs_0.6.2 hms_1.1.2 bit64_4.0.5
## [29] data.table_1.14.2 R6_2.5.1 rmarkdown_2.16 bookdown_0.28
## [33] purrr_0.3.4 magrittr_2.0.3 codetools_0.2-19 htmltools_0.5.3
## [37] ellipsis_0.3.2 stringi_1.7.8 cachem_1.0.6 R.oo_1.25.0References
De Comité, Francesco, François Denis, Rémi Gilleron, and Fabien Letouzey. 1999. “Positive and Unlabeled Examples Help Learning.” In International Conference on Algorithmic Learning Theory, 219–30. Springer.
Denis, François, Rémi Gilleron, and Fabien Letouzey. 2005. “Learning from Positive and Unlabeled Examples.” Theor Comput Sci 348 (1): 70–83.
Li, Chen, and Xue-Liang Hua. 2014. “Towards Positive Unlabeled Learning for Parallel Data Mining: A Random Forest Framework.” In International Conference on Advanced Data Mining and Applications, 573–87. Springer.