Section 1 Data engineering
1.1 purf package installization
See instructions on the GitHub webpage.
1.2 Retrieving P. vivax protein variables
In Bash:
echo "create database pfpv_reverse_vaccinology" | mariadb -u <dbuser> -p
mariadb -u <dbuser> -p pfpv_reverse_vaccinology < ./other_data/pfpv_reverse_vaccinology.sqlOverall database schema:
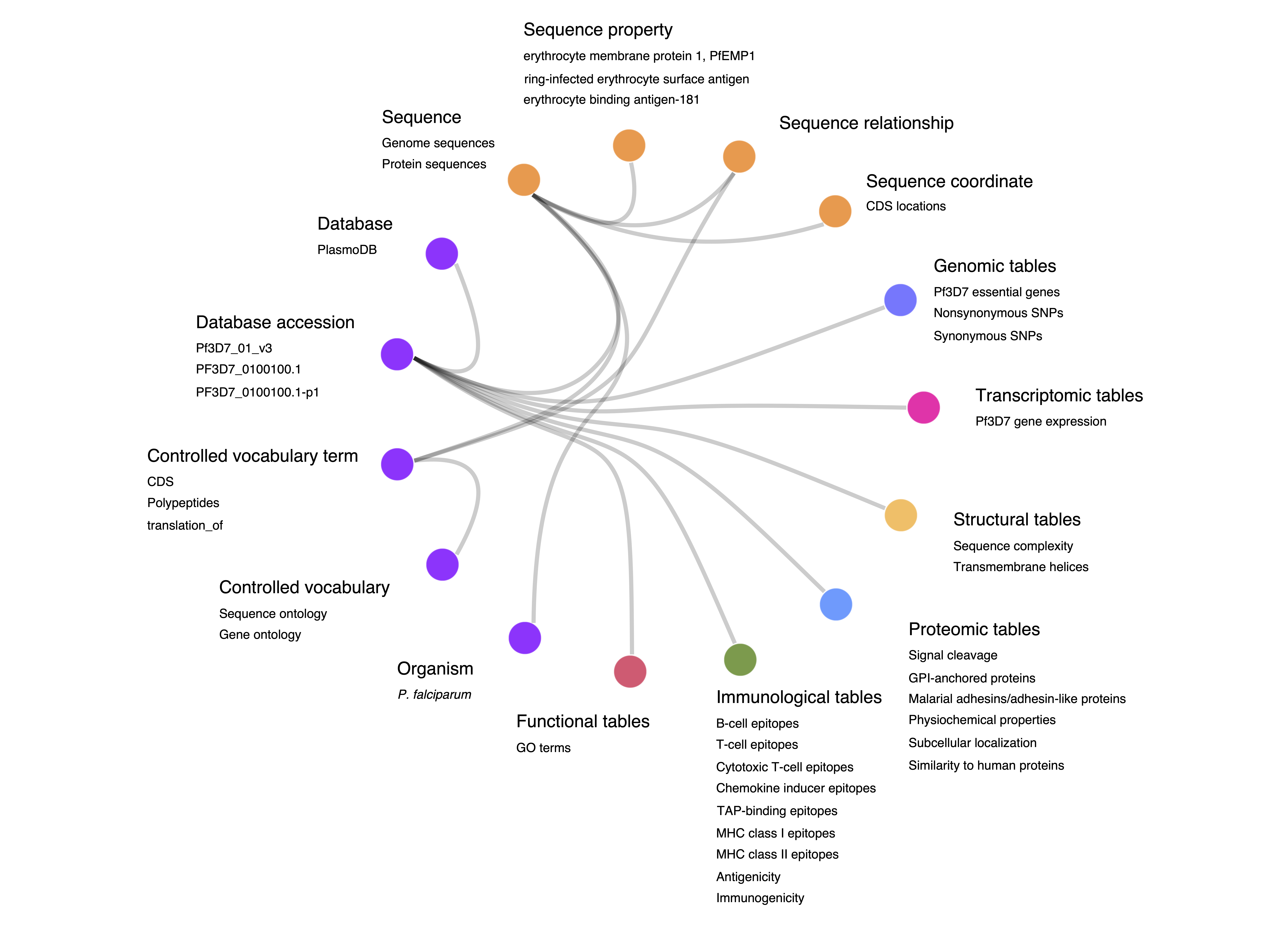
In R:
library(RMariaDB)
library(DBI)
library(rlist)output_path <- "./other_data/pv_assembled_data.csv"
db <- dbConnect(RMariaDB::MariaDB(), user = "root", password = "", dbname = "pfpv_reverse_vaccinology")
get_data <- function(table_name, db) {
sql <- sqlInterpolate(db, "SELECT * FROM ?table", table = dbQuoteIdentifier(db, table_name))
return(subset(dbGetQuery(db, sql), select = -c(id)))
}
# protein ID and transcript ID map table
id_map <- dbGetQuery(db, 'SELECT dbxref_1.accession AS accession, dbxref_1.dbxref_id AS protein_id FROM dbxref AS dbxref_1
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature AS feature_1 ON dbxref_1.dbxref_id = feature_1.dbxref_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN cvterm ON feature_1.type_id = cvterm.cvterm_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature_relationship ON feature_1.feature_id = feature_relationship.subject_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN feature AS feature_2 ON feature_relationship.object_id = feature_2.feature_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN dbxref AS dbxref_2 ON feature_2.dbxref_id = dbxref_2.dbxref_id
LEFT OUTER JOIN organism ON feature_1.organism_id = organism.organism_id
WHERE feature_1.is_obsolete = 0 AND cvterm.name = "polypeptide" AND organism.species="vivax_P01"')1.2.1 Immunological data sets
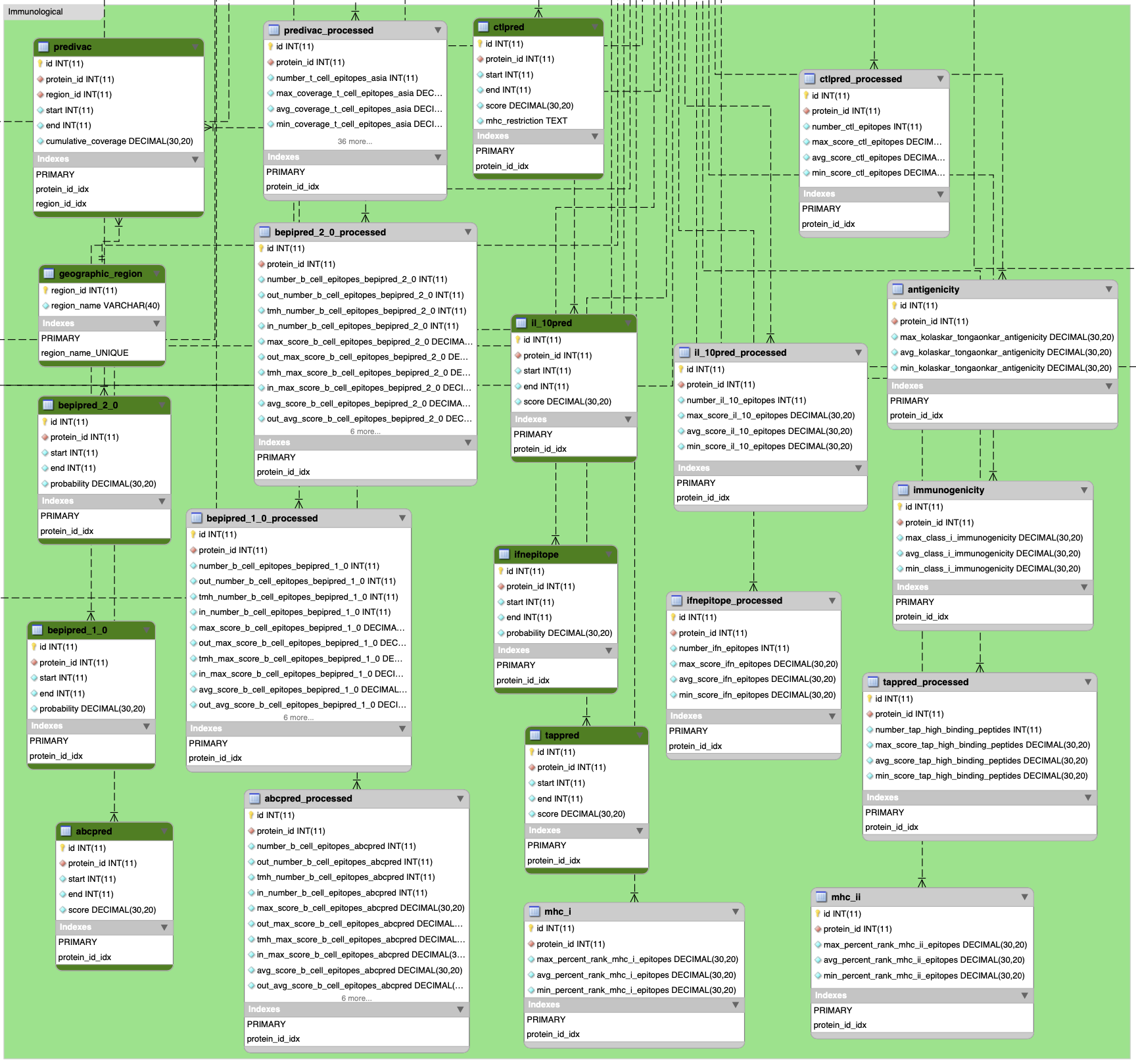
In R:
immu <- list()
# predivac_processed result for T-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("predivac_processed", db))
# bepipred_2_0 result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("bepipred_2_0_processed", db))
# bepipred_1_0 result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("bepipred_1_0_processed", db))
# abcpred result for B-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("abcpred_processed", db))
# ctlpred result for cytotoxic T-cell epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("ctlpred_processed", db))
# il_10pred result for interleukine-10 inducing epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("il_10pred_processed", db))
# ifnepitope result for IFN-gamma inducing epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("ifnepitope_processed", db))
# tappred for high binding affinity epitopes toward the TAP transporter
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("tappred_processed", db))
# mhc_i for MHC class I epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("mhc_i", db))
# mhc_ii for MHC class II epitopes
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("mhc_ii", db))
# antigenicity
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("antigenicity", db))
# immunogenicity
immu <- list.append(immu, get_data("immunogenicity", db))
# merge immunological data sets
immunological_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in immu) {
immunological_ds <- merge(x = immunological_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.2 Proteomic data sets
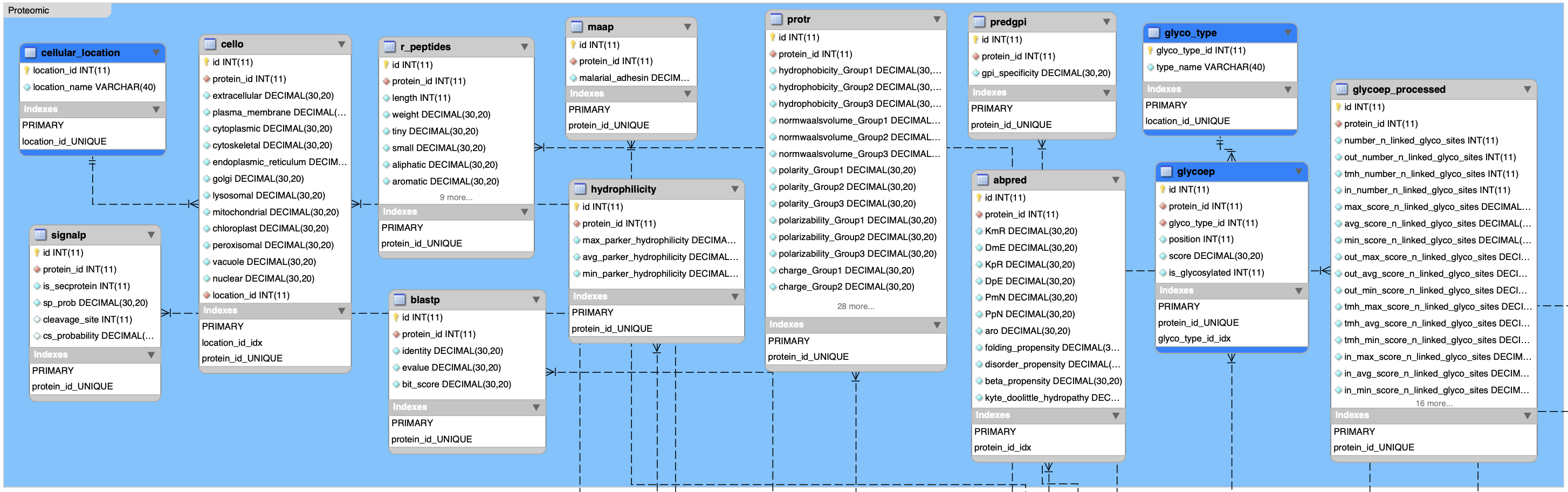
In R:
pro <- list()
# cello result for subcellualr localization
pro <- list.append(pro, subset(get_data("cello", db), select = -c(location_id)))
# maap result for malaria adhesin/adhesin-like proteins
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("maap", db))
# peptides result for physicochemical properties
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("r_peptides", db))
# protr result for physicochemical properties
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("protr", db))
# hydrophilicity
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("hydrophilicity", db))
# predgpi result for gpi anchors prediction
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("predgpi", db))
# signalp result for signal cleavage prediction
pro <- list.append(pro, subset(get_data("signalp", db), select = -c(is_secprotein, cleavage_site, cs_probability)))
# abpred results for amino acid compositions and other variables
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("abpred", db))
# glycoep results for N-linked and O-linked glycosylation
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("glycoep_processed", db))
# blastp result for similarity to human proteins
pro <- list.append(pro, get_data("blastp", db))
# merge proteomic data sets
proteomic_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in pro) {
proteomic_ds <- merge(x = proteomic_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.3 Structural data sets
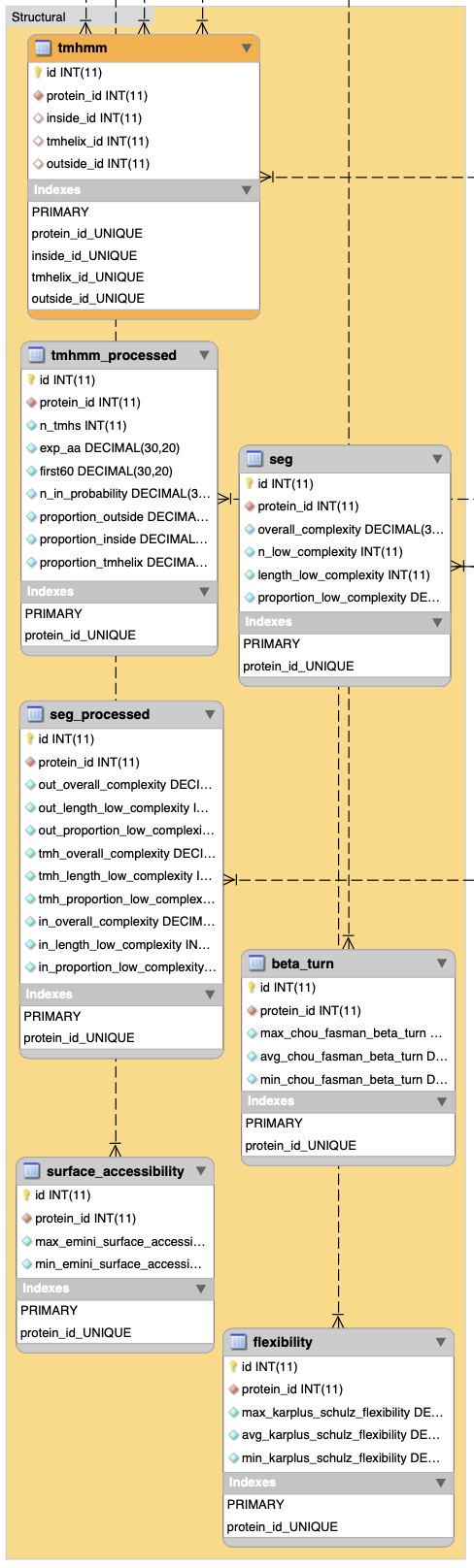
In R:
struc <- list()
# tmhmm result for transmembrane helices prediction
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("tmhmm_processed", db))
# seg result for sequence complexity
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("seg", db))
# seg + tmhmm result
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("seg_processed", db))
# b_cell_epitope_methods for structural predictions
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("beta_turn", db))
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("surface_accessibility", db))
struc <- list.append(struc, get_data("flexibility", db))
# merge structural analysis data sets
structural_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in struc) {
structural_ds <- merge(x = structural_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.4 Genomic data sets
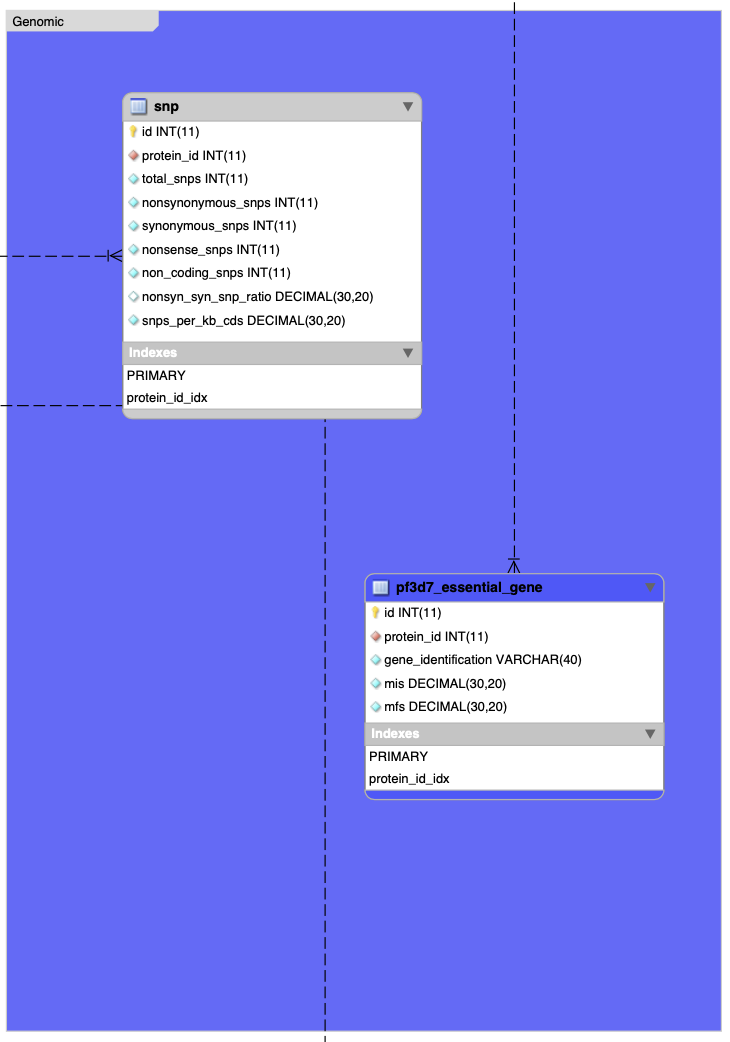
In R:
geno <- list()
# snp result
geno <- list.append(geno, get_data("snp", db))
# merge structural analysis data sets
genomic_ds <- id_map["protein_id"]
for (ds in geno) {
genomic_ds <- merge(x = genomic_ds, y = ds, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
}1.2.5 Final assembly
In R:
# prepare predictor variables
data <- merge(x = immunological_ds, y = proteomic_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = data, y = structural_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = data, y = genomic_ds, by = "protein_id", all = FALSE)
data <- merge(x = id_map, y = data, by = "protein_id", all.x = TRUE)
accession <- data$accession
data <- subset(data, select = -c(protein_id, accession))
rownames(data) <- accession
# write to output
write.csv(data, output_path)
# close database connection
dbDisconnect(db)1.3 Generating ML input
In R:
response_var <- read.csv("./other_data/pv_antigen_labels.csv", row.names = 1)
predictor_vars <- read.csv("./other_data/pv_assembled_data.csv", row.names = 1)
ml_input <- merge(x = response_var, y = predictor_vars, by = "row.names", all = TRUE)
row_names <- ml_input$Row.names
ml_input <- subset(ml_input, select = -c(Row.names))
rownames(ml_input) <- row_names
# write to output
write.csv(ml_input, "./data/supplementary_data_2_pv_ml_input.csv")sessionInfo()## R version 4.2.3 (2023-03-15)
## Platform: x86_64-apple-darwin17.0 (64-bit)
## Running under: macOS Big Sur ... 10.16
##
## Matrix products: default
## BLAS: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2/Resources/lib/libRblas.0.dylib
## LAPACK: /Library/Frameworks/R.framework/Versions/4.2/Resources/lib/libRlapack.dylib
##
## locale:
## [1] en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8/C/en_US.UTF-8/en_US.UTF-8
##
## attached base packages:
## [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
##
## other attached packages:
## [1] rlist_0.4.6.2 DBI_1.1.3 RMariaDB_1.2.2
##
## loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
## [1] Rcpp_1.0.10 bslib_0.4.2 compiler_4.2.3 jquerylib_0.1.4
## [5] highr_0.10 R.methodsS3_1.8.2 R.utils_2.12.2 tools_4.2.3
## [9] digest_0.6.31 bit_4.0.5 jsonlite_1.8.4 evaluate_0.21
## [13] lifecycle_1.0.3 R.cache_0.16.0 pkgconfig_2.0.3 rlang_1.1.1
## [17] cli_3.6.1 rstudioapi_0.14 yaml_2.3.7 xfun_0.39
## [21] fastmap_1.1.1 styler_1.9.1 knitr_1.42 vctrs_0.6.2
## [25] sass_0.4.6 hms_1.1.3 bit64_4.0.5 glue_1.6.2
## [29] data.table_1.14.8 R6_2.5.1 rmarkdown_2.21 bookdown_0.34
## [33] purrr_1.0.1 magrittr_2.0.3 codetools_0.2-19 htmltools_0.5.5
## [37] cachem_1.0.8 R.oo_1.25.0